Thrombosis And Pregnancy: A Dangerous Couple

Thrombosis and pregnancy are a dangerous couple. However, with an early diagnosis and the adoption of certain measures, it is possible to deal with this problem.
We must remember that blood circulation can be affected by the presence of a clot. This produces what is known as thrombosis. Knowing its characteristics will help prevent the disease.
During pregnancy, the chances of suffering from thrombosis increase. This is because the pregnant woman’s blood is more susceptible to forming clots due to some clotting or placental changes.
In addition, the uterus increases in size, decreasing vascular circulation, especially in the lower limbs. Find out why thrombosis and pregnancy are situations that don’t coexist well.
What is a thrombosis?
The clot that forms inside blood vessels is known as “thrombosis”. More specifically on the edges. Therefore, it is one of the possible complications that can occur in pregnancy.
Thrombosis is a more common condition in women who are sedentary, obese, who have varicose veins or over 30 years of age. The risk of suffering from a thrombosis increases as the pregnancy progresses.
Thrombosis can appear superficially or in the veins inside. They can mean serious complications as clots can break loose, obstructing blood flow and causing a pulmonary embolism. It is believed that pregnancy increases the chances of having thrombosis by 10%.
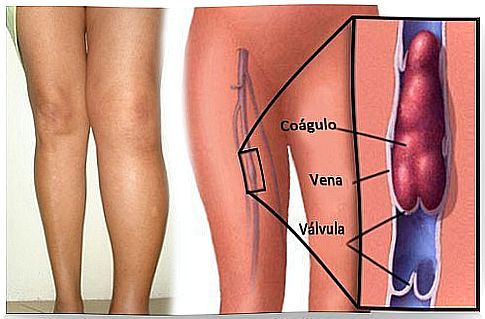
Symptoms of thrombosis in pregnancy
During pregnancy, fluid retention in the body’s cells, especially in the legs, is very common. However, this inflammation may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Fever.
- Cough and chest pain.
- Burning and swelling in the calf.
- Tachycardia and difficulty breathing.
- Redness on the affected extremity.
- Sharp pain that extends from the thighs to the calf.
Possible causes of thrombosis in pregnancy
Although pregnancy is already a major risk factor, this situation can be combined with other possible causes:
- Obesity.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
- Hormonal changes.
- Intestinal changes.
- Cesarean section or premature birth.
- Blood clotting disorders.
- Pressure caused by fetal growth.
Helping to lessen the effects of these causes will greatly reduce your chances of suffering from thrombosis during pregnancy.
Pregnancy complications when having thrombosis
Having thrombosis during pregnancy can lead you to suffer the following consequences:
- Limitation of fetal growth.
- Miscarriages until the first trimester of pregnancy.
- Placental abruption. It consists of the partial or total separation of the placenta and the uterine wall. Furthermore, with this complication there is a significant loss of blood, putting both their lives at risk.
Treatments for thrombosis in pregnancy
Treatment will depend on the type of thrombosis and what causes it may have:
- 1. Superficial thrombosis. In this case, the treatment will be based on prophylactic measures, such as lifting the legs, physical exercise, using bands or special elastic stockings. Sometimes this treatment is supplemented by taking an anticoagulant such as aspirin.
- Deep thrombosis. For this treatment, heparin-type anticoagulant drugs are used intravenously and subsequently subcutaneously.
How to prevent thrombosis during pregnancy?
Basically, the best way to avoid this pathology is to increase physical exercises that promote blood circulation. It can also be complemented with the following methods:
- Avoid work at high temperatures.
- Maintain a balanced, healthy and nutrient-rich diet.
- Avoid sitting for a long time or resting for a long time.
- Take small, frequent walks totaling at least 150 minutes a week.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing that impedes normal blood flow.
- Avoid standing with your legs crossed for a long time, as this makes the venous return difficult.
- Take drugs prescribed by your doctor to prevent or treat thrombosis in pregnancy.
- If your doctor recommends rest, ask for suggestions on how to keep your legs elevated.
- Keep a very specific control in relation to coagulation tests, Doppler echo, etc.
- Another great alternative is to closely monitor the feed. Thus avoiding foods with a lot of sodium.
In short, thrombosis and pregnancy are a dangerous couple, but with an accurate diagnosis and proper care, it is a situation that can be resolved.
At the same time, it is necessary to closely observe the symptoms and drink enough water, as this will considerably reduce the chances of having thrombosis.