Scabies In Children: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment – I’m A Mom
Scabies in children is a common and contagious skin disease. Although it can affect children of any socioeconomic level, people living in poverty or overcrowded conditions are at much greater risk of contracting it.
Also called scabies, the risk of getting it is greatest in young children, the elderly and people with weakened immune systems.
Causes of Scabies in Children
Scabies develops because of a mite, Sarcoptes Scabiei, which spreads through direct skin-to-skin contact. The mite only stays alive out of skin contact for about 24 to 36 hours, so transmission through fomites such as clothing, sheets and mattresses is limited.
The infected child develops a hypersensitivity reaction to the mite, its eggs and its faeces. This can be triggered 3 weeks after exposure to the infectious agent.

Scabies was declared a neglected skin pathology by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2009. In turn, it only takes 10 minutes of skin-to-skin contact for the mites to be transmitted.
Symptoms of Scabies in Children
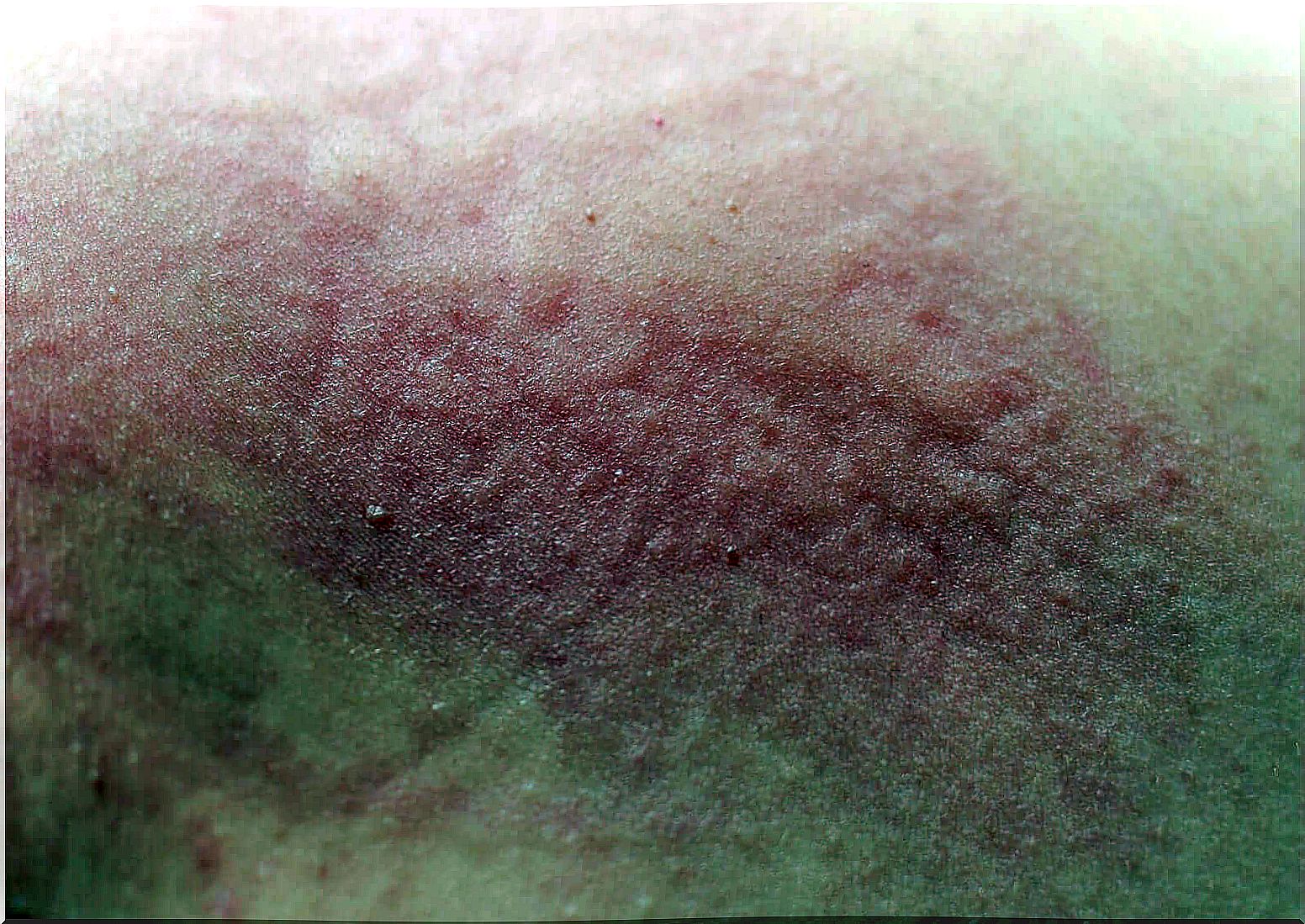
The presentation of symptoms of this parasitic infection includes erythematous papules and general itching that usually increases overnight.
According to a publication by the Society of Pediatrics of Asturias , Spain, lesions in children are located on the palms of the hands, on the soles of the feet and on the cephalic pole.
However, in adults, the locations vary and prevail between the fingers of the hands, in the flexion of the wrist, in the elbows or armpits, or in the genitals and breasts.
All these symptoms take about 3 weeks after contact with the mite to manifest. However, when it comes to reinfections, clinical manifestations can be seen within a few hours.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of scabies is made based on the observation of the skin lesions by the specialist physician at the time of the consultation. In turn, the professional will conduct a detailed questionnaire to discard the patient’s background.
However, if one wants to confirm the diagnosis, mites, eggs or feces can be seen from a skin scrape under a microscope.
If the diagnosis is uncertain, a biopsy of the lesion may be considered in order to obtain greater certainty. However, this type of procedure does not usually occur very often.
Differential diagnosis
Scabies is often confused with other itchy rashes:
- Eczema.
- Impetigo.
- Tinea corporis .
- Prurigo nodularis.
- Dermatitis.
- Pruritic pathologies.
- Psoriasis.
However, in scabies it is possible to observe the paths made by the mite during its locomotion. These are called tunnels. These are sinuous white lines that indicate the excavation of the parasites.
Treatment Options for Scabies in Children
People who live in the same house, asymptomatic or symptomatic, must be treated simultaneously to avoid transmission or reinfection. The main reason to treat people without symptoms is that they can take weeks to manifest.
Permethrin
Topical 5% permethrin lotions or creams are the first-line treatment. Additionally, they should be applied to the skin from the neck to the toes, usually overnight. The next day they must be rinsed.
Even in the case of babies with scabies, the creams should also be applied to the face. One week after the application, the procedure is repeated to kill the larvae that have been born during this period. In addition, patients and family members should be made aware of the likelihood that the itching will persist for a long time.
Ivermectin
Oral ivermectin is another available option for the treatment of scabies in children. Thus, for children over 10 years, an initial dose is given and another dose after one week.
This therapeutic option is recommended because of the following advantages:
- For your convenience, membership fees increase.
- Safety.
- Ease of administration, reducing the likelihood of misuse or improper application.
- Few adverse effects.
Other variations
It is necessary to disinfect sheets, mattresses, towels and clothing. Other therapeutic options are topical lindane, 5% precipitated sulfur, malathion, and topical ivermectin.
5% precipitated sulfur in petroleum jelly is indicated for pregnant women and young children because of its safety, although the odor and uncomfortable application may compromise the treatment.
Ultimately, even with proper treatment, the signs and symptoms may persist for several weeks to disappear completely.
The good prognosis of the disease is related to the treatment of the patient and his close contacts. Thus, if the treatment is not carried out, the scabies can spread to other people in the community.